AI is moving fast in the coding space, and new tools keep showing up with bold promises. I’ve spent my entire last month trying out a wide range of these coding tools to see how reliable they are in real tasks and how much help they actually provide.
If you’re trying to understand which AI coding tools are worth paying attention to, this guide will help. I’ve pulled together the tools that performed well in my tests and the tasks where they delivered good results.
The Landscape of AI for Coding
AI now supports almost every part of the coding workflow. You can go from quick inline suggestions to full assistants that write features, review pull requests and handle bigger changes across a project. The common use cases include:
Code Completion and Suggestion: Quick inline hints in your editor, like Tabnine, that predict the next token, line, or small block based on context.
Code Generation and Block Creation: Chat-style or command-style tools that can write functions, classes, tests, or small services from a short brief.
Code Review, Debugging, Refactoring, and Security: Coding assistants that read pull requests, find bugs, suggest safer patterns, and point out risky dependencies or weak spots.
Domain Specific Coding: Models tuned for domains like SQL, analytics, financial systems, medical coding, EHR logic, etc. that know the usual schemas and rules.
Local or on Prem and Privacy Focused Options: Tools you run on your own hardware or inside a private cloud to keep source code and data in a controlled environment.
Best AI Models for Coding
A good coding model should support the languages you use, understand large files and long conversations, and work smoothly inside your editor or CI setup. It also needs to handle your code safely and make sense from a cost point of view, whether you work solo or in a team.
The right choice also depends on how you work. Some people want quick one-off prompts. Others need steady pair-programming support. Some prefer fully automated agents that run workflows on their own.
Here are the four main groups to think about:
Claude by Anthropic: Claude 3.5 Sonnet was already near the top of coding benchmarks. It solved about 64% of internal agent coding tasks, well ahead of older Claude models. Recently, Anthropic released Claude Opus 4.5. It now leads major coding tests like SWE-Bench Verified and is pitched as “senior engineer” level for complex code and long-running tasks.
GPT Models by OpenAI: GPT-5, GPT-5.1, and Codex are very strong all-rounders and excellent for debugging, writing new code, and working with tools. OpenAI’s docs and third-party tests highlight them as a clear step up from GPT-4o for coding, long context, and tool use.
Local / Open-Source Models: Projects like DeepSeek, GLM‑4.6, Qwen3-Coder, StarCoder2, and newer Code Llama variants give you solid multi-language coding help. You can run on your own hardware or cloud, with no vendor data sharing and more control over tuning. Qwen3-Coder is great for local use, and StarCoder2 and Code Llama 3 are strong general choices.
Agent-Style and Domain Models: On top of the base models, there are tools built around “agents” that can plan and run multi-step coding tasks. For example, Cursor, Windsurf (with its Cascade mode), and Google’s Gemini Agents for Dev. There are also smaller models tuned for specific jobs, like SQL helpers, test generators, or tools for compliance and security checks.
| Model / Family | Type | Strengths | Trade-Offs | Best Use Case |
| Claude Opus 4.5 / Claude 3.5 Sonnet | Hosted, commercial | Strong at complex code, long context, and multi-step tasks, with good safety defaults. Great on coding benchmarks like SWE-Bench and high agent-style coding results. | Paid for serious use, rate limits apply, no self-hosting. | Teams or solo devs who want a “thinky” pair programmer for big refactors, tricky bugs, and long design docs. |
| GPT-5.1 / GPT-4 (OpenAI) | Hosted, commercial | Great all-round coding, strong tool use, deep ecosystem (ChatGPT, Copilot, many SaaS tools). GPT-5.1 is good for coding and complex instructions, and other models show up in free or cheaper tiers. | Data and security controls depend on the plan. Some tasks can be costly at high volume. | Everyday coding, debugging, and “explain this code” work across many languages and stacks. |
| Gemini 3 Pro (Google) | Hosted, commercial | Strong reasoning and coding inside Google’s dev tools. Good multi-modal context (logs, docs, UI) and early “agent” features through Gemini Agents and Antigravity.) | Best results inside the Google stack. Full features are often behind specific products and accounts. | Teams already using Google Cloud, Vertex AI, or Antigravity for end-to-end development. |
| DeepSeek-Coder / Qwen3-Coder | Local/open source | High benchmark scores for code, multi-language support. Optimized for local inference with quantized builds and active community support. | You manage infra, updates, and security. Quality can lag top hosted models on very hard tasks. | Companies that need on-premise or VPC-only setups, or power users who want control and low marginal cost. |
| StarCoder2 / Code Llama 3 | Local/open source | Good performance on common languages, flexible licenses. It can be fine-tuned or stacked with tools, runs well on mid-range GPUs. | Not always on par with the best closed models for tricky reasoning or huge contexts. | General local coding aid, teaching tools, and experiments where you want to tinker. |
| Agent-style tools (Cursor, Windsurf, Gemini Agents, etc.) | Tools built on top of models | Can work across whole repos, run tasks like “add feature X” or “migrate this service,” and loop on feedback. Often integrate tightly with Git, tests, and terminals. | Still needs careful review, can be slow or costly for big tasks. Quality depends on both the base model and the tool. | Teams that want more auto-pilot coding help, hackathons, and complex refactors across many files. |
Top AI Tools for Coding
Here are the AI coding tools that stood out in my testing, what each one does well and when they’re worth using.
1. GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot is an AI “pair programmer” that lives inside your editor and suggests code in real time as you type. It turns natural-language comments and partial code into full functions, tests, and patterns across many languages.
I tried a palindrome checker in Python. GitHub Copilot immediately produced a compact, readable function that normalized the string by removing spaces and lowercasing it, then compared it to its reverse. It even added simple inline comments explaining each step.
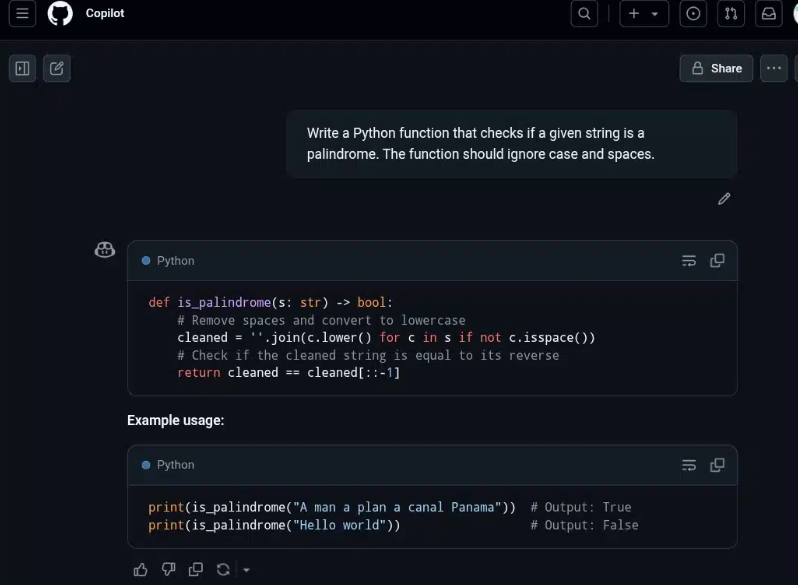
Next, I asked Copilot to write a function that fetches data from an API. It generated a modern async/await wrapper inside a try/catch. It included a sensible error logging and a clear fallback value when the request failed. The code was minimal, expressive, and structured so I could drop it straight into a real project without much modification.
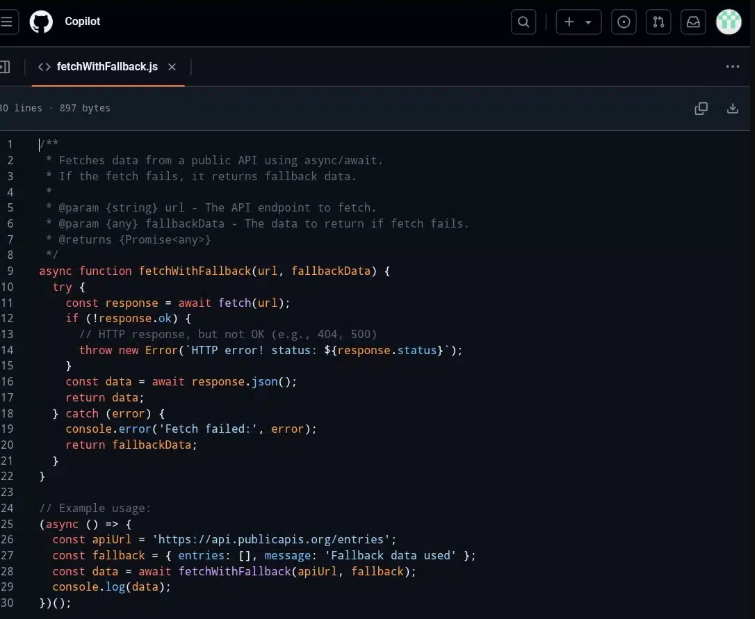
For a slightly more involved scenario, I tried file I/O and text processing. Copilot generated a script that opened the file safely, normalized the text, and used collections.
Counter to count word frequencies, a very Pythonic approach. It then sorted and printed the top 10 results with their counts, and annotated the main steps with simple comments. Even someone new to Python could follow the logic from top to bottom.
Copilot is great in terms of context. It doesn’t just look at the current line, but considers the whole file, related files you have open, and the surrounding framework. In React, it could infer sensible component structures and Material UI Grid patterns from the imports and existing code. For propTypes, it pulled the right shape from a related file and suggested a correctly nested shape definition.
On the backend, even though GitHub says PHP isn’t a “first-class” language for Copilot, the results were surprisingly good. In Laravel, it suggested appropriate authorization messages based on the surrounding code. It guessed Eloquent model fields inside a switch for query filters, and filled in parameters based on the variables already in scope.
GitHub Copilot Features
AI Pair Programming: Real-time code suggestions as you type, based on comments or partial code.
Language and Framework Support: Optimized for popular languages like JavaScript/TypeScript, Python, Go, C#, C++, and more, but usable with many others.
Deep Context Use: Considers current file, related files, libraries, and patterns to generate relevant code and even tailored messages or prop types.
IDE Integration: Extensions for VS Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, Neovim, and others.
Shortcut-Driven Workflow: Accept with Tab, cycle suggestions, or open a full suggestion panel for alternatives.
GitHub Copilot Pricing
- Copilot Free: $0, limited completions and chat.
- Copilot Pro: ~$10/month or $100/year.
- Pro Plus: $39/month or $390/year for scaling.
- Business and Enterprise: Per-seat pricing for teams with admin controls, policy management, and org-wide configuration.
- Dramatically fewer browser searches for common patterns and utility functions.
- Smarter autocompletion than typical IDEs, when multiple related files are open.
- Best suited for experienced developers who can quickly judge whether a suggestion is safe and correct.
- Helps you focus on architecture and integration rather than boilerplate.
- Can hallucinate incorrect or out-of-date library usage. You still need to read and understand the code.
- Risky as a learning crutch for beginners who may lack the skills to vet suggestions.
My Honest Take: Copilot is closest to “magic autocomplete” for working developers. It nails boilerplate, common patterns, framework glue, and cross-file context awareness. But it will happily hallucinate outdated APIs or subtle bugs. So you must treat it as a smart assistant, not an authority.
2. Tabnine
Tabnine is a privacy-first AI code assistant for dev teams and enterprises that care about governance, deployment control, and faster code.
It plugs into popular IDEs (VS Code, JetBrains family, Eclipse, Visual Studio) and can be deployed as SaaS, in your own VPC, on-prem, or even fully air-gapped. So code never has to leave your perimeter.
Tabnine focuses on privacy guarantees and agent-style capabilities. Code review, testing, and other workflow agents can support the full SDLC, not just autocomplete.
I used Tabnine across Java, Python, and C++ to generate, explain, and fix code, as well as create tests and timing logic. Tabnine continually leveraged rich context and full chat history.
Tabnine’s Protected model handled iterative workflows (like C++ quicksort + tests). The external models showed how Tabnine’s deep context passing lets them recognize existing code, explain it, and suggest improvements rather than blindly regenerating solutions.
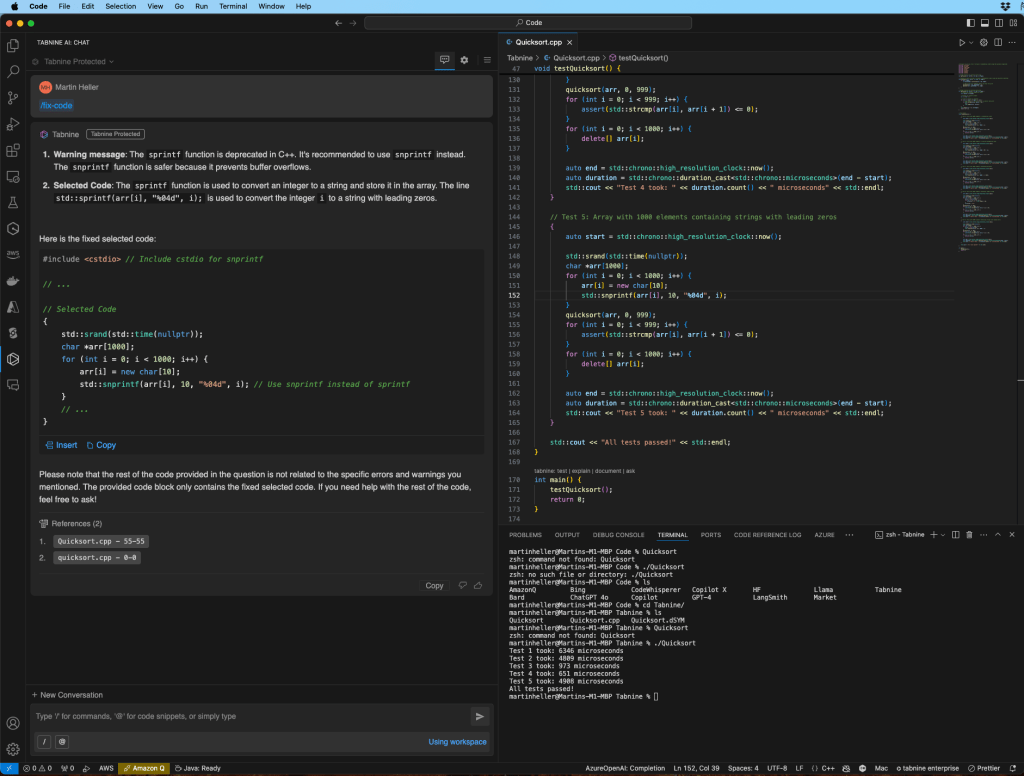
Then I tried the more “agentic” features: leaning on the Code Review/Test behavior to catch missing tests and surface issues before review. These agents are clearly still evolving, but they did a decent job flagging some basic edge cases, suggesting test scaffolding, and generating docstrings.
Tabnine really differentiates itself when you look at where it runs. It keeps everything in a private install (VPC or on-prem Kubernetes) or even fully air-gapped, while still getting AI suggestions. It puts it in a different category from cloud-only tools like GitHub Copilot.
Tabnine Features
Privacy-First Design: “No-train, no-retain” posture for customer code. Context is used for inference and then discarded. Explicit statements that user code isn’t fed back into training.
Flexible Deployment: Secure SaaS, single-tenant SaaS, VPC deployment, on-prem Kubernetes, and fully air-gapped options for enterprises that need strict control over data flows.
AI Coding Agents: Beyond inline completions, Tabnine markets Code Review and Test agents (and related SDLC helpers) to help with testing, documentation, and quality enforcement across IDE, CLI, and CI.
IDE and Language Coverage: Broad plugin support for VS Code, JetBrains, Eclipse, and Visual Studio. Plus, coverage for dozens of languages and frameworks. Third-party write-ups cite “80+ languages” in regular use.
Enterprise admin and SSO: Role-based admin console, SCIM/IdP sync, policy controls over which models are available, and tight control of private endpoints for chat and coding models.
Tabnine Pricing
Tabnine has one agentic platform pricing edition that costs $59.
- If you need to keep code inside your perimeter, Tabnine’s private and air-gapped deployments are a major differentiator versus cloud-only competitors.
- Great governance and model control. Enterprise admins get fine-grained control over users, roles, and which agents are allowed.
- If your team uses a mixed fleet of IDEs, Tabnine’s broad plugin support roll out a single assistant across VS Code, JetBrains, and legacy tools.
- Agent narrative fits SDLC workflows. Especially in regulated environments that care about repeatable processes.
- The agent features (Code Review/Test, etc.) are powerful but still evolving. They can require process changes and careful tuning to add value.
My Honest Take: Tabnine is private, self-hostable, and air-gapped. If you’re in finance, healthcare, defense, or any regulated space, that’s great to use. Its suggestions are solid, and the “agent” features are still maturing. Great for enterprises, and overkill for solo devs who just want faster autocomplete.
3. Codex by OpenAI (AI ChatBot)
Codex is a chat-first tool by OpenAI, and once you’re in, you’re pushed through mandatory MFA and then asked to authorize the Codex GitHub app for whichever organizations and repositories you want it to touch.
From there, Codex clones your repos into its own execution sandboxes. Inside those sandboxes, it can run commands, make changes, and create branches on your behalf.
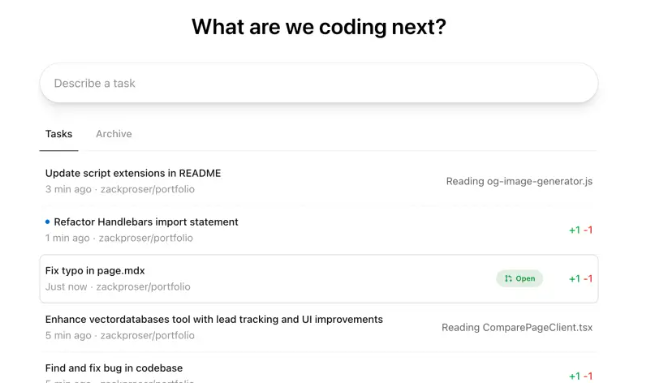
If you live in a world of dozens of public and private repositories, it feels fantastic. You can hop between projects, queue up work, and keep everything inside one unified interface. If you only actively use one or two repos, though, the setup overhead may feel heavier than just dropping into an LLM chat or relying on an AI-powered editor like Cursor.
The overall design assumes that chat is your primary control surface. You can tell Codex what you want done in natural language, and it orchestrates git operations, shell commands, and pull requests from there.
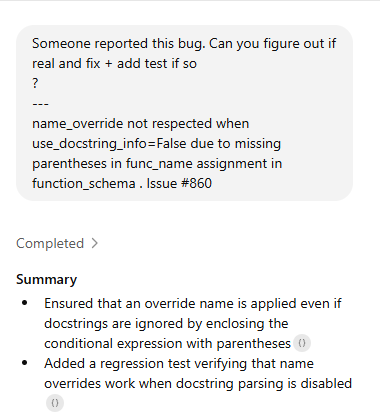
I dropped the bug report into Codex and asked it to confirm whether name_override was really being ignored when use_docstring_info=False.
Codex traced the issue to the missing parentheses in func_name inside function_schema, and proposed a one-line fix. Then helped me scaffold a regression test to prove the override still works with docstring parsing disabled
Codex Features
GitHub-First Integration: You authorize the Codex GitHub app for your orgs/repos. Codex then clones your repositories into isolated sandboxes where it can run commands, create branches, and modify code directly.
Chat-Based Follow-Ups: Each task has its own chat thread. Once initial work is done, you can dive into that thread, see what Codex has done, and request follow-up changes in natural language.
PR Creation and Descriptions: When you’re satisfied with the branch, you can ask Codex to open a pull request. It will handle the git plumbing and auto-generate a PR description for you.
Logs and Command Transparency: For each task, you can inspect raw logs showing the shell commands and operations Codex is running. It gives transparency into the changes it’s making inside your repos.
Mobile-Friendly Usage: The interface works on mobile, so you can check logs, approve PRs, and issue follow-ups from your phone. It supports more “untethered” workflows.
Codex Pricing
Codex doesn’t have its own separate pricing tier. It’s bundled as a feature inside standard ChatGPT plans (Plus, Pro, Business, and Enterprise).
If you’re already paying for ChatGPT, you simply get access to the Codex agent and tools as part of that subscription. Each tier mainly differs by how many local messages or cloud tasks you can run in a 5-hour window.
- Multi-Tasking: If you juggle many repos and have a backlog of small tasks, Codex shines as an orchestration and automation layer to flush out tedious work.
- Natural-Language Control Surface for Git + Shell: You don’t have to context-switch between terminals, editors, and GitHub tabs. Describe what you want, and Codex does the mechanical steps.
- Maintenance-Level Work: Copy edits, style fixes, minor refactors, and other low-risk chores are where Codex feels most reliable and time-saving.
- Supports Workflows: Everything is centralized in a chat-first UI that works on mobile. You can review, iterate, and ship small changes while you’re not at your main machine.
- Opaque Error Handling: Tasks and PR creations sometimes fail without clear explanations. It makes trust and debugging harder.
- Inconsistent Code Quality for Complex Work: For larger refactors or intricate changes, Codex’s output often needs significant human correction.
- No Network Access in Sandboxes: Codex can’t install new packages or update dependencies from the internet. It blocks many real-world tasks (e.g., fixing dependency issues and regenerating lockfiles).
MY Honest Take: If your main issue is the volume of small, repetitive development chores across multiple repos, Codex offers a powerful, GitHub-native way to offload that work. If you’re hoping for a fully autonomous engineer for complex features and refactors, it’s not quite there yet. But the trajectory suggests it could grow into that role over time.
4. Claude Code by Anthropic
Claude Code is Anthropic’s shot at bringing agent-style coding into the command line. Instead of a full GUI editor, you run a Claude command in a directory and let the model edit files, run tests, and poke at your repo from a plain terminal.
After using it to build a small “Roast my LinkedIn” app from scratch, the verdict is mixed. It’s smart in what it can do, but it’s held back by the interface and pricing.
Claude Code is suitable for boring jobs you avoid. You can set up Pytest, wire a basic CI workflow, draft tests, or add a reading mode or server-side search to a personal app.
You hand it a chore you do not feel like doing, give it room to take a stab at the solution, then review and adjust.
Claude Code Features
CLI-based AI Assistant: Runs from the terminal, works over your repo while you supervise, and it encourages a talk-and-skim style of coding.
Strong for “Vibe Coding”: Works well when you want to think out loud, try ideas, and let the model explore options.
Great for Chores: Setup tasks, tests, small extensions, and mechanical changes become easier to delegate.
Self-Correction Over Time: It often notices issues from earlier steps and fixes them as it goes, and reduces how much you need to micro-manage.
Codebase Aware Help: Can answer questions about structure and logic, then act on that understanding.
Git History Operations: Searches history, helps resolve merge conflicts, and can create commits and PRs.
Claude Code Pricing
Claude Code is bundled with Claude Pro for individuals at $17/month on annual billing ($20/month month-to-month).
Max 5x at $100/month and Max 20x at $200/month. Both include Claude Code and give you much higher usage for larger projects.
Team seats are $150 per person per month, with a 5-user minimum, and include Claude Code and admin controls. Enterprise is custom-priced. Find more about the pricing here.
- Handy for extending existing features or backends where UI polish is not a must.
- Agentic abilities around git and repo-level operations are functional experiments.
- Good match for side projects and non-critical work for momentum and perfect efficiency.
- Costly compared to competitors.
- Lower supervision by design makes it a poor fit for strict standards or high risk changes.
My Honest Take: Claude Code is fantastic for setting up tests, wiring CI, adding small features, or cleaning up scripts from the terminal. It’s like a thoughtful junior dev who can work over your repo without you babysitting. The downside is cost and control. It’s not the tool you give free rein on mission-critical systems or big refactors yet.
5. Cursor
Cursor is a full IDE built on top of Visual Studio Code, with deep AI integration. It embeds large-language-model assistance into your programming workflow. You can write, refactor, debug, and explore code with natural-language prompts instead of manually typing every line.
Under the hood: autocomplete + multi-line edits, full-file or multi-file generation, context-aware chat, and even codebase-wide understanding.
Cursor looks and feels a lot like VS Code. But I found that simple tasks like toggling sidebars, opening the terminal or chat panel, or doing side-by-side diff comparisons felt awkward or missing. So, your muscle memory will also need some re-training!
But I loved its AI‑first, context‑aware approach. I used Cursor to build a simple Python script for data analysis. I gave it a prompt to clean and visualize a dataset using pandas and matplotlib.
In just a minute, it generated the necessary code, loaded the dataset, cleaned it, and produced a line plot.

The AI handled the mundane parts of coding. I didn’t have to worry about writing boilerplate code like setting up pandas or matplotlib. It just worked.
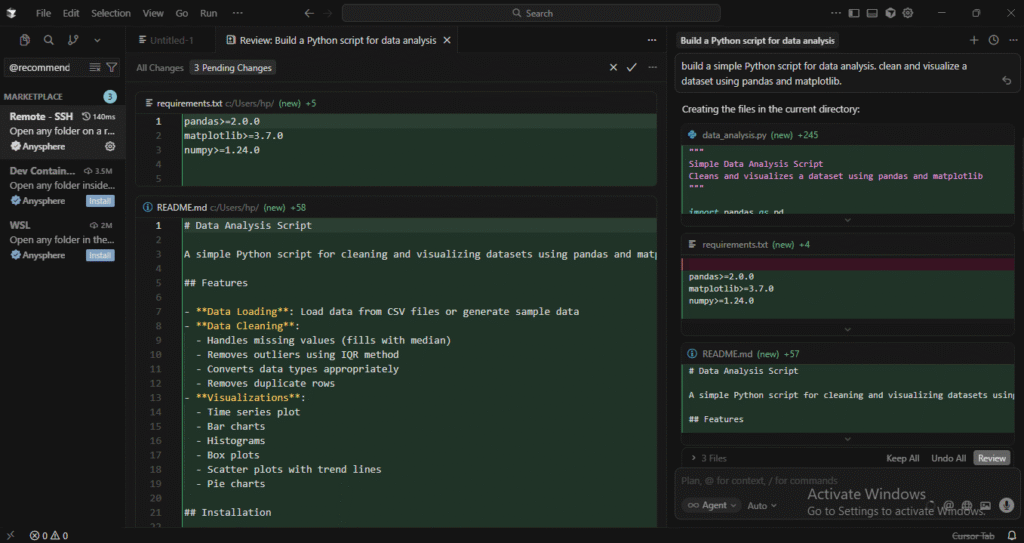
For data processing or visualization, Cursor is an incredible time-saver. It’s particularly useful when you’re looking to move fast without worrying about the syntax, as it handles the basic structure for you.
Next, I wanted to test how well Cursor can help with a more complex machine learning task. I asked it to set up a basic neural network using TensorFlow to classify images from the MNIST dataset.
In minutes, the AI generated a fully functional neural network and the necessary preprocessing steps and model architecture. I didn’t need to dive into documentation or search for code snippets.
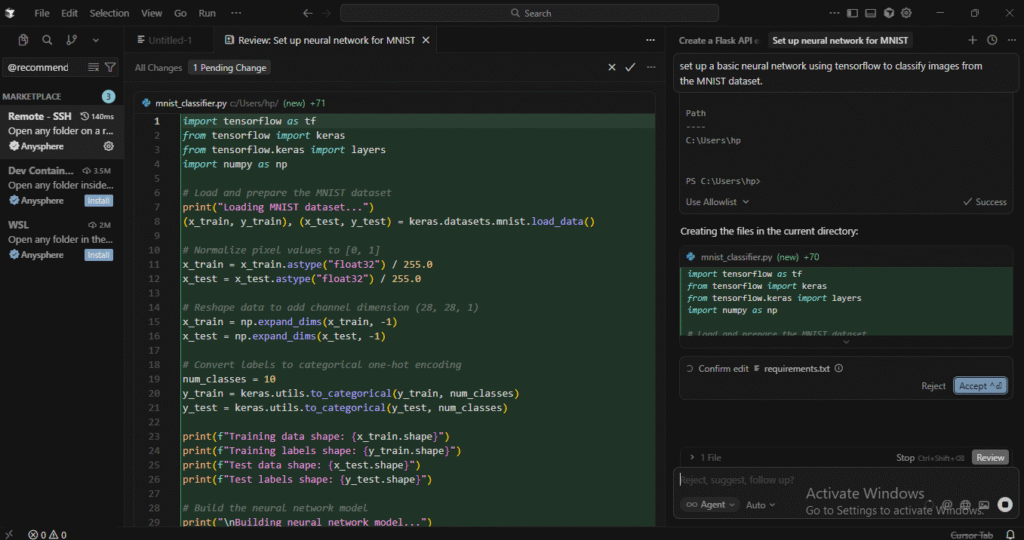
I also tweaked the model by adding more layers and adjusting the learning rate. Each time, it adapted quickly to my requests, made adjustments to the code, and kept the overall structure intact.
Cursor Features
Intelligent Code Completion: Cursor’s autocomplete and code suggestions involve line-by-line autocomplete, multi-line edits, context-aware suggestions, and even entire function or module generation. You can even get a Python function to fetch from an API and handle errors.
Project-Wide Context: Cursor understands your entire project. The imports, dependencies, architecture, and naming conventions. Then suggestions become more relevant and reduce “context-blind” mistakes.
Composer Mode and Agent Mode
- Composer Mode: You pick specific files (or modules), describe what you want done (e.g., “refactor this service,” “add error-handling”), and it applies edits. It shows diffs so you can review before committing.
- Agent Mode: More ambitious. You can prompt Cursor to roam across your codebase (or generate a new structure), run commands, or even handle shell tasks. In its 2.0 version (2025), Cursor introduced support for running up to eight parallel “agents,” each operating in an isolated copy of your codebase to avoid conflicts.
Built-In Debugging: There is real-time bug detection, suggestions, and code reviews. If something seems off (missing imports, syntax, inconsistent patterns), it can flag it or suggest fixes.
Familiar Environment + Extensibility: Since Cursor is essentially a VS Code fork, you retain access to VS Code’s ecosystem. The extensions, linters, formatters, version control, and more.
Cursor Pricing
Cursor uses a subscription-based pricing model. There are different tiers:
- Free: $0/month (Limited access, basic features)
- Pro: $20/month (Extended limits of agents)
- Pro+: $60/month
- Ultra: $200/month (priority access to features)
- Fast coding, especially for repetitive tasks or boilerplate code generation. It took seconds for basic CRUD endpoints, utility functions, and configuration files.
- Refactor across files with ease. For example, large-scale cleanups, naming consistency, and structural changes.
- Composer mode gives the user control (you see diffs, accept/reject). The Agent mode offers bold automation when needed.
- Project-wide context gives smarter suggestions.
- Quality and consistency vary for domain-specific code.
- Some complex use cases may not be fully addressed by the AI assistant.
My Honest Take: Cursor is amazing when you lean into its workflow. Let it understand your whole project, then use Composer/Agent modes for refactors and new features. For greenfield scripts, data tasks, and typical web apps, it can feel like cheating in the best way. But quality can wobble on niche stacks. Also, it’s unnecessary if you just want lightweight autocomplete.
6. Windsurf Editor
Windsurf is an AI-native IDE that replaces the usual stack of editor, terminal, browser, and separate AI chat with one connected workspace. It builds around an always-on agent called Cascade that tracks what you are doing and offers help with real context.
Install it and import your usual preferences. Open a project, and you are ready to write code without digging through config files or chasing extensions.
The layout will feel familiar if you come from VS Code or JetBrains. But there are an extra Cascade panel and a preview or deploy bar that appears when you work on frontend code.
To test Windsurf, I asked Cascade to “make me a playable 2048 app with smooth animations” in an existing project folder.
It scanned the directory, created a fresh styles.css file, and checked index.html and game.js. Then, it reported that there was already a full 2048 implementation in place.
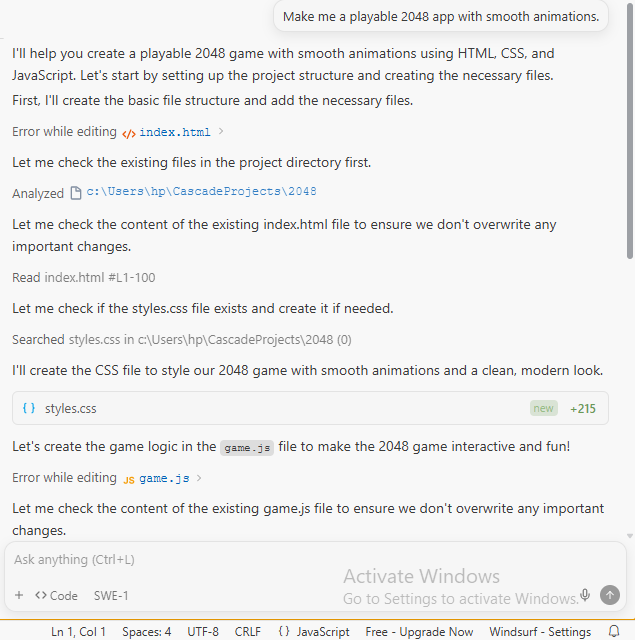
From there, I opened index.html in the browser and played several rounds, checking keyboard and touch controls, score tracking, and the smooth tile movements and merges.
The main difference from a simple autocomplete tool is how much the agent sees. Cascade keeps track of files, terminal commands, clipboard content, and even some browser activity. It can rename components across a project, follow errors from the terminal into the correct file, and suggest fixes that touch multiple files at once.
The dev-to-deploy flow is a strong point. When you edit a Next.js or similar frontend project, you can spin up a live preview inside the IDE, click on elements, then let Windsurf jump you to the matching JSX or component and propose edits. When something is ready, a simple Deploy button deploys it to Windsurf’s hosting. It becomes handy for prototypes and personal projects that do not need full CI.
Windsurf Features
Cascade Agent with Project-Wide Context: Tracks your actions across files and terminal, suggests edits, runs commands, and handles multi-step code changes.
Tab for Intent-Aware Autocomplete: Windsurf Tab goes beyond line-by-line suggestions. It fills in imports, boilerplate, and missing pieces based on what you are building.
In-Editor Previews and One-Click Deploys: See your frontend running beside your code, click on UI elements to jump to their source, then deploy to a Windsurf URL when ready.
Inline AI Commands in Code and Terminal: Use natural language to refactor sections, write functions, or run shell commands from inside the editor so you stay in one place.
Plugins and MCP Support: If you prefer other IDEs, there are plugins for JetBrains, VS Code, Neovim, and Xcode. Plus a Model Context Protocol layer that lets the agent pull context from tools like GitHub, Slack, Stripe, and databases.
Windsurf Pricing
Windsurf’s pricing is split into clear tiers:
- A Free plan with 25 prompt credits per month and unlimited tabs.
- A Pro plan at $15 per month with 500 credits.
- Teams at $30 per user with shared controls and analytics.
- Enterprise plans with 1,000 credits per user and extra security options like RBAC and hybrid deployment.
Add-on credits are available on paid tiers.
- Strong for multi-file work. Cascade shines when you are refactoring or debugging across many files instead of a single script.
- Faster feedback loop for web apps. Live previews and quick deploys cut out a lot of tab-hopping when building frontend features.
- All-in-one environment. Editor, AI chat, terminal, previews, and deploys live together, so you spend less time wiring tools.
- The credit model can be confusing. Windsurf tracks “flow actions” for internal steps inside a single request. It makes reasoning about usage harder than simple “requests per month.”
- Live previews use extra memory and can slow things down in larger codebases.
My Honest Take: Windsurf shines when your work spans multiple files, terminal commands, and quick frontend deploys. Cascade having full context across editor + terminal + preview makes refactors and debugging smoother. The credit model and flow actions can feel confusing, and heavy previews can slow down bigger projects.
7. Gemini 3 by Google
Gemini 3 feels like a clear step from “smart chatbot” to “digital coworker. It acts like a real coworker who can code, plan, and run tools. You can build things, work with messy data, and handle projects easily.
I used Antigravity, Google’s agent layer on top of Gemini 3. It’s like a group of agents that can read files, write code, browse the web, and open tools.
I drop requests into an Inbox in plain English, and the agents turn that into plans, scripts, and UI changes. For example, I pointed it at a folder with all my past AI posts and asked it to build a site listing my predictions and checking which ones turned out right.
Gemini read the files, drafted a plan, did web research, wrote code, opened my browser to test the site, and then handed the result back for review.
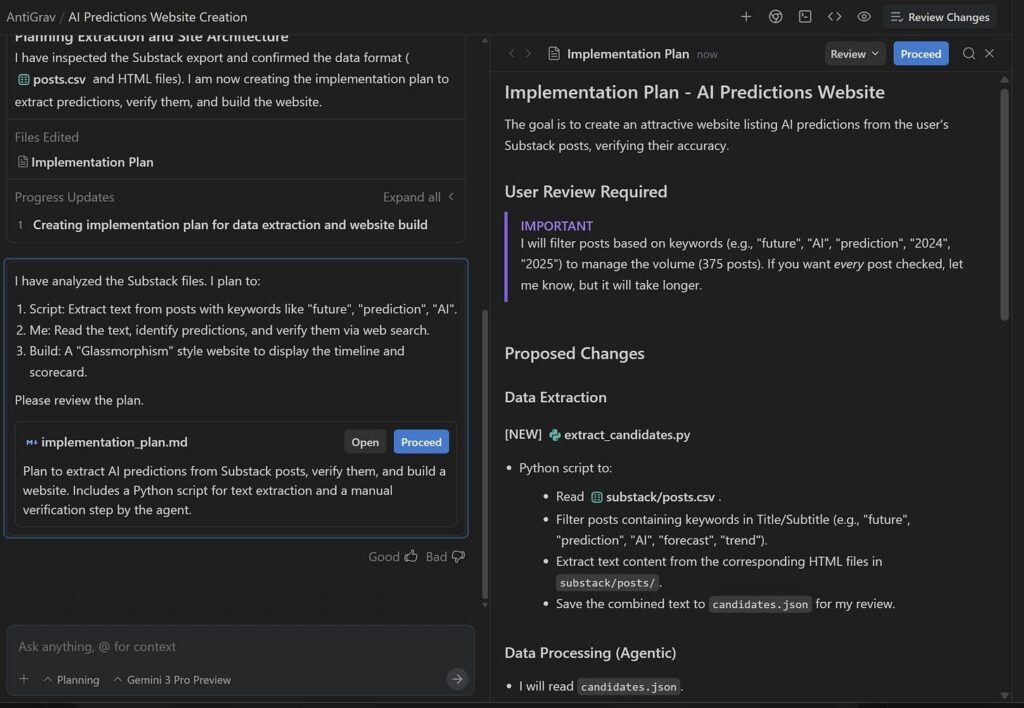
It did not vanish into a black box. It showed me its plan and paused for approval at key steps. The mistakes I saw were not wild hallucinations, more like the kind of judgment slips you see from a new tool that mostly gets it but needs nudges.
Gemini 3 Features
Agentic Coding and Automation: You can assign tasks in plain English, and agents write code, run scripts, read files, and control the browser to complete end-to-end work.
Inbox-Based Workflow: Each task lives in its own thread where you can see the plan, approve steps, and check outputs.
Strong Planning and Tool Use: Gemini breaks big goals into smaller actions. It knows when to ask permission, and stitches code and web actions together.
Research and Analysis Help: It can clean old datasets, design a basic study, run nontrivial analysis, and format results into a draft paper or report.
Creative Coding: Small web games to dashboards and simple sites, it can move from idea to working code in one pass and then refine with follow-up prompts.
Gemini 3 Pricing
Free gives you basic Gemini 3 access with about 10k tokens a month.
Pro is $20 per user per month, bumps you to around 100k tokens, adds multimodal features, and more.
Enterprise starts higher per month and is built for larger teams that need steady, high-speed performance, reliability, custom model training, and a dedicated support contact. Find more about pricing here.
- Handles long-running, multi-step tasks where code, files, and the browser all connect.
- Let you stay at the level of goals and review, and it handles the busy work.
- Adapts well to feedback, much like a capable grad student or junior engineer.
- Still needs supervision, on methods and final judgement calls.
- Agent flows are powerful but not yet “set it and forget it” for high-stakes work.
My Honest Take: Gemini 3 (with Antigravity-style agents) is best when you need planning plus execution. It’s excellent for glue work, data cleaning, prototypes, small tools, and project scaffolding. But it still needs supervision and is not yet a “set it and forget it” system for complex or regulated code.
8. Replit (for Vibe Coding)
Replit is a browser-based IDE with built-in AI-assisted coding. It can take you from idea to deployed app without touching local setup. You open a URL, pick a language, and start coding. Replit handles environment, hosting, and collaboration for you.
Its AI layer embeds into the editor to provide inline completions, code generation, explanations, and refactors while you type.
Replit really stands out due to “vibe coding” and collaboration. Multiplayer editing in the browser, live previews, and AI make it easy to build projects together at hackathons, bootcamps, and in classrooms.
I used Replit AI to build a simple landing page and an AI coding blog, and gave it a simple prompt to create a landing page.
In a few seconds, it generated a complete page: a big hero headline, a short description, and a CTA button wired up on the screen. I didn’t touch any code. I just hit “Run” and saw it live in the preview.
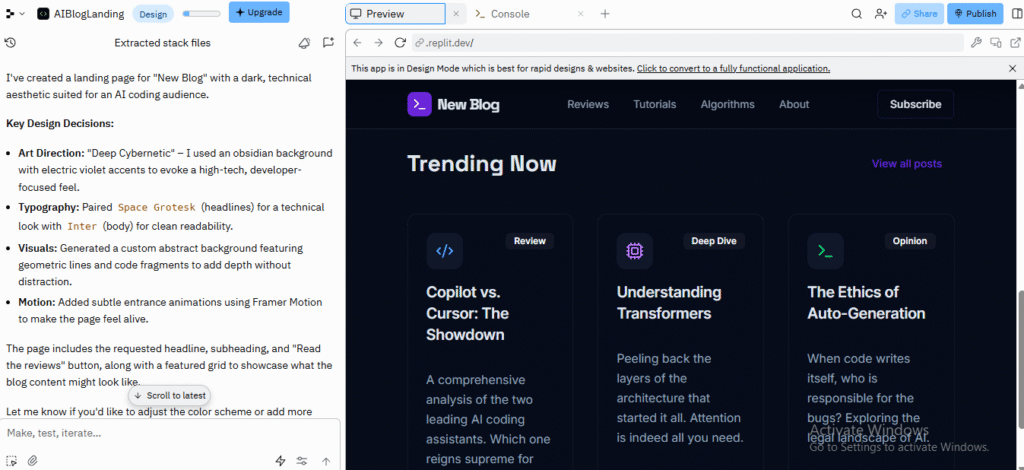
Then, I followed up with a style change. The layout didn’t change dramatically, but the colors, fonts, and spacing shifted enough that it started to feel more like a real page instead of a boring default template.
I was able to push it toward a very specific aesthetic without touching every line manually.
Takeaway: For UI-heavy tasks where you care more about feel than pixel-perfect design, Replit AI actually works well as a “vibe translator.” You can describe the mood, and it gives you a starting point. The more you riff with it, the closer it gets to what you had in your head.
Next, I wanted to see if Replit could help me build something playful and slightly chaotic: an interactive canvas toy that spawns animated shapes on click.
The AI scaffolded a clean little HTML/JS file: click handler, random size/position/color, CSS animations. From there, it was fun to treat the AI like a creative partner:
- “Make the shapes fade in and out, like bubbles.”
“Change the overall vibe to ‘lofi chill’ and use muted colors, slower animations.”
Everything runs instantly in the browser, it became a feedback loop: click around, decide what feels off, fire a quick prompt, watch the toy morph.
The Agent sometimes broke other parts of the site while trying to fix something. It also overrided user intent and force into extra debugging/iterations after “helping.” So, you need to keep it in check.
Replit Features
Multi-Language Support: You can code in 50+ languages (Python, JavaScript, C++, etc.) without any installation.
AI-Assisted App Generation: The Replit Agent can build multiple app types:
- Web apps
- Data visualization tools
- 3D games with Three.js
- Agents and automations
It can go beyond front-end scaffolding and generate more complete applications from prompts.
Built-In Storage and Database: Replit includes:
- A built-in database for structured data and relationships
- App storage for unstructured data like images and documents
- Production databases in beta for live apps
External App and Design Imports: You can import projects from Bolt, Lovable, GitHub, and even Figma frames, which the Agent converts into React apps.
SSH and Local Sync: Replit can connect to your local environment via SSH so changes in your IDE stay synced with your Repl, like file/folder changes.
Version Control: It supports Git workflows and GitHub integration. You can import repos, edit them, and push changes back.
App Publishing and Deployments: Replit handles hosting with options like autoscaling deployments, static sites, scheduled deployments, and reserved VMs for always-on apps.
Replit Pricing
As of late 2025, Replit’s pricing is plan-based + usage-based. You can pick a tier, get some credits, then pay extra if you go beyond that.
- Starter (Free): $0/month (Basic limited access)
- Core: $20–25/month
- Teams: $35–40/user/month
- Enterprise: Custom Pricing
Realistically, using Replit AI heavily pushes you toward a paid plan once you start deploying or running bigger apps.
- Fast path from idea to running app. Especially for beginners.
- Helpful AI help for brainstorming, learning, and generating code.
- Adapts well to feedback, much like a capable grad student or junior engineer.
- The credit model and Agent 3 pricing cause frustration and anxiety.
- The Agent can be unreliable at scale, ignore instructions, or introduce bugs.
- Even with specific directions, it doesn’t always follow them.
My Honest Take: Replit is perfect when you wanna run in the browser without setting up local infrastructure: hackathons, classrooms, quick demos, or playful experiments. The AI feels like a fun, creative partner for UI tweaks and small JS toys. For bigger systems, the credit model, agent quirks, and cloud constraints become frustrating.
9. Lovable
Lovable is like a “superhuman full-stack engineer” in your browser. You can describe your app in natural language, and it handles front-end, back-end, database, and deployment in one place.
It’s suited to:
- Non-technical users to build apps without hiring developers.
- Early-stage founders validating ideas with quick prototypes and MVPs.
- Product teams and designers who want to turn ideas or UI screenshots into working prototypes.
- Developers who want to offload boilerplate and UI work but still own and edit the code.
It’s best for simple apps: dashboards, internal tools, AI utilities, landing pages, auth systems, workflow automation, role-based access, and document-generation tools.
Lovable’s workflow is:
- Plan: Describe your idea or start from a template.
- Prompt: Write natural language instructions or upload screenshots or designs.
- Generate: Lovable creates the app structure and code.
- Debug: It helps find and fix errors with AI-driven tools.
- Deploy: One-click deployment with a shareable link.
Under the hood, it generates React + Tailwind (Vite) frontends, sets up backends, and wires databases and hosting without manual setup.
Key Integrations:
Supabase: Automatic auth, PostgreSQL, file storage, server functions, and analytics configured via natural language prompts.
GitHub: Live repo sync, edits in Lovable push to GitHub and vice versa.
Custom Domains: You can point your own domain to Lovable apps for branding and SEO.
Multiplayer Workspaces: Teams can collaborate in a shared workspace with centralized billing.
There’s also a Chat Mode Agent that doesn’t edit code directly. But can reason about your project, inspect logs, search files, query the database, and help plan or debug in multi-step fashion.
For a “hackathon demo” style project, I tried an idea notebook that suggests tags and summaries.
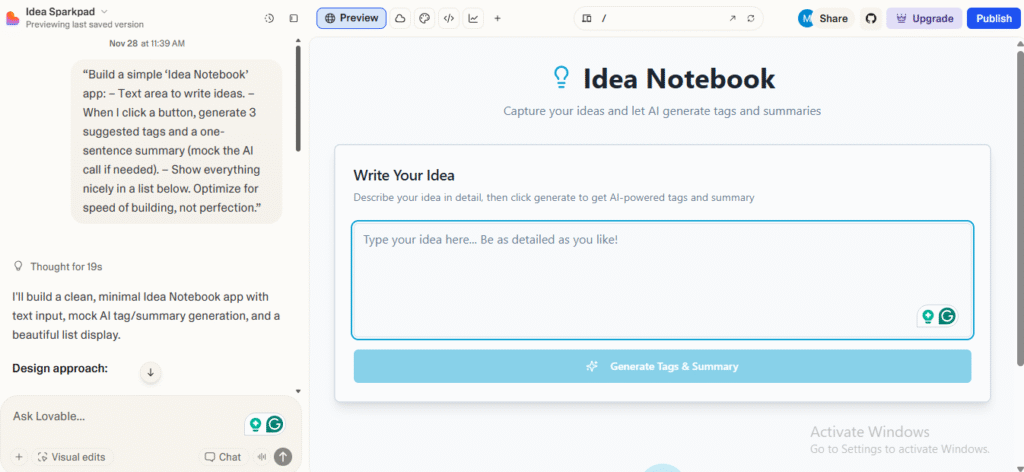
The process involved:

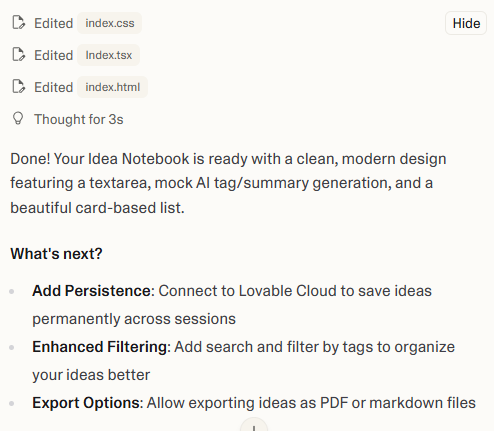
Here I paid attention to two things:
- How quickly I could get to a demo-worthy state.
- How AI handled “fake AI” (mocking calls) vs any real integration.
It set up a basic form, list rendering, and a mock “AI” function that randomly generated tags and summaries from the note content. After that, it was trivial to extend:
- Swap the mock with a real API call later.
- Add filters.
- Tweak the layout for mobile.
It is very much the hackathon sweet spot: you get a believable AI-powered demo in one tab without getting lost in tooling.
If your goal is to go from nothing to “this looks like a real product” in under an hour, Loveable makes that path pretty smooth, when you let its own AI do the repetitive wiring.
The Visual Editor is a big differentiator. It is a Figma-like interface where you tweak the actual UI (colors, sizes, layout) with real-time feedback and maintain clean Tailwind/JSX code behind the scenes.
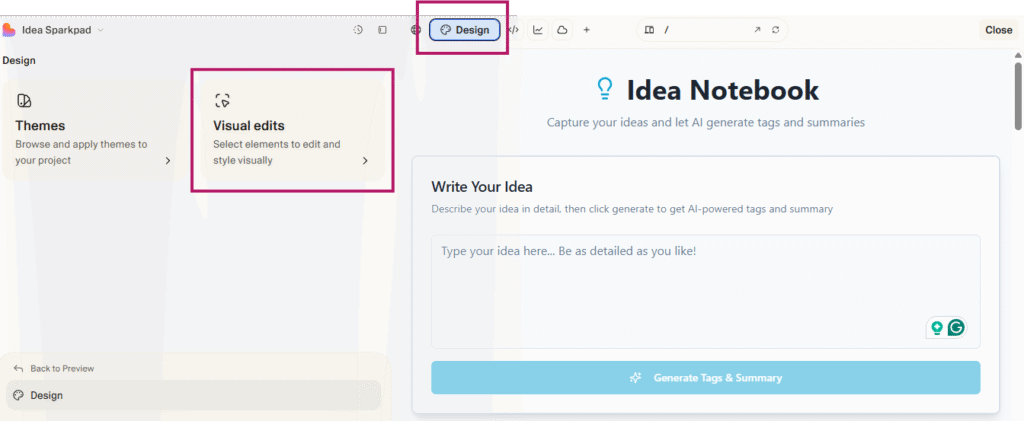
It uses AST transformations, client-side Tailwind generation, and a mapping between UI elements and source code. It keeps everything editable and maintainable.
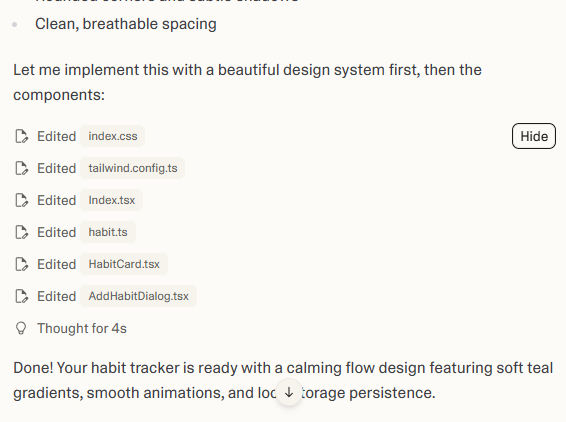
I also built a habit tracker app, with a creative twist, and added some interactive design elements.
The app started with simple functionality, as I asked, checkboxes, habit tracking, and a removal option. You could easily see Loveable’s creative direction.
The process involved:

Lovable delivers speed for simple to moderately complex apps. You can generate landing pages and CRUD apps in minutes. And even more advanced setups (like dashboards with auth and charts) come together much faster than hand-coding.
The platform excels at front-end generation and turns descriptive prompts into visually pleasing interfaces with animations.
On larger, more complex projects, the platform’s limitations show. Like most LLM-based systems, Lovable often delivers a 60–70% solution. Great scaffolding and structure, but requiring additional optimization, manual debugging, and professional review before being production-ready.
Lovable Pricing
Lovable’s pricing is based on message (credit) limits, not tokens.
- Free plan (5 messages per day)
- Pro plan ($25/month)
- Business plan ($50/ month)
- Enterprise plan (custom)
When using, messages from the free daily allowance are used first. Then your monthly paid credits kick in. Credits reset each billing cycle.
- Very easy to build simple apps and dashboards from prompts.
- Generates good-looking UI components (especially frontend/TypeScript).
- Simple to hook up Supabase for persistence and basic backends.
- Excellent for non-technical users who want basic tools without hiring devs.
- Useful for technical users as a quick way to get UI/utility scaffolding.
- Struggles with complex, agentic, or highly dynamic apps.
- Layout and behavior sometimes drift away from what you requested via prompts.
- Changes via prompt consume credits. No drag-and-drop editor to quickly rearrange components.
My Honest Take: Lovable is awesome for spinning up decent-looking full-stack apps from prompts. Especially dashboards, internal tools, and simple SaaS-style utilities. But like most LLM builders, it usually gets you 60–70% of the way. Layout quirks, edge cases, and complex logic still need a real developer.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns of AI Coding
Security Risks and Data Privacy
When you let an AI tool write or suggest code, there’s a risk the output might include security holes. AI-generated code may contain flaws and vulnerabilities like injection risks or insecure default patterns that slip past casual review.
If your project deals with sensitive data, like user records, health info, or financial details, treat AI-generated code as untrusted until you review it carefully.
Bias in AI-Generated Code
AI models learn from large datasets. If those datasets have biases, historical or demographic, those biases can get baked into the code or logic the AI generates. The code might produce or reinforce unfair behavior, or mishandle data in unpredictable ways.
Intellectual Property and Licensing Issues
The code AI spits out may come from patterns seen during training. And those patterns might be under licenses. It’s often unclear whether the generated code violates licensing terms
Tips and Best Practices for Implementation
If you decide to use AI coding tools, treat them as an assistant, not a replacement.
Select Right Tool and Model
Run through a checklist: what languages or frameworks does your team use? Do you need on-premises or cloud tools? How important is data privacy? Do you need code review and auditability? How critical is code quality and security. Tools vary a lot in those aspects. The tool should support your stack and let you control data flow.
Pilot First, Full Rollout Later
Don’t throw the AI tool at your entire codebase at once. Pick a small, motivated team or a non-critical project. Run a pilot to test impact. Track metrics like how much coding time you save, how many bugs slip in, or how often generated code needs manual fixing. Use those results to decide if you scale up.
Workflow Integration
Treat AI suggestions like first drafts. Keep regular code reviews, static analysis, and manual checks in place. Incorporate the AI tool into your IDE plugins, CI/CD pipelines, code review workflows, and team coding standards. Use AI for boilerplate or scaffolding. But don’t trust it for security-critical, domain-specific logic without review.
Adapt For Domain-Specific Needs
If you work in a niche domain (say, medical coding, regulated data, or legacy systems), you get custom configurations or fine-tuned models. The AI tool should understand your domain context and follow your coding standards. Double-check AI-generated code for compliance, licensing, and security.
Measure ROI and Progress
Track metrics over time: coding time saved, bug rates, security issues, code review times, developer satisfaction, and team adoption. That helps justify the tool to stakeholders if you’re working in a team or company.
Use Local/Offline Deployment When Privacy Matters
If you deal with sensitive or regulated data (healthcare, finance, personal records), use offline or self-hosted AI models. It reduces the risk of data leaks or compliance issues.
Extra Care for Hackathons, SMBs, Or Niche Domains
For small teams or rapid-build environments, AI tools can accelerate prototyping. But always include manual audits and security reviews before deploying, when handling sensitive parts or user data.
Think Ahead: Future Readiness
AI tools will evolve, multi-agent workflows may arise, and best practices will shift. Stay alert, be ready to adapt. Build a culture of regular review, security audits, and ethics awareness.
Final Thoughts
AI is quickly becoming a standard part of the coding workflow, but the best tool for you depends on your language, your projects and the level of support you need. Whether you use ChatGPT, Claude or something more focused like GitHub Copilot, it should fit your work and respect your privacy, budget and team setup.
The safest way to start is with a small pilot. Try it on one project, track how much time it saves and check the impact on code quality. Once you see what works, you can adjust your workflow and bring these tools into more of your day-to-day work with confidence.